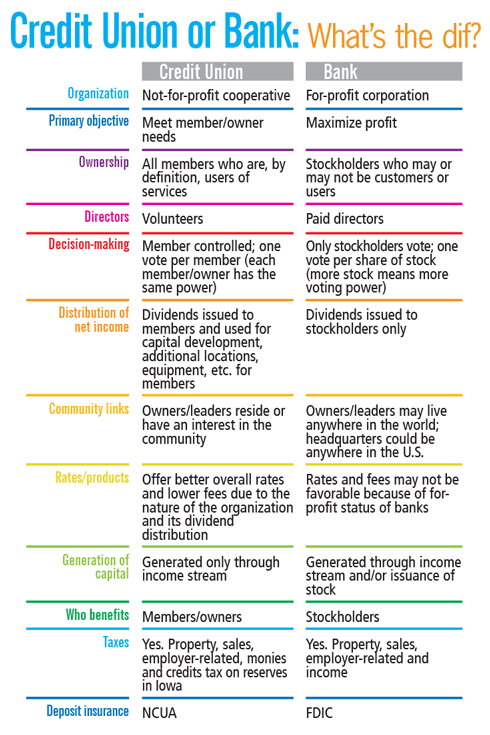
Dupaco exists to serve you, not to make a profit. Unlike banks and other financial institutions, we do not issue stock or pay dividends to outside stockholders. Our earnings are returned directly to our member-owners — in the form of lower loan rates, higher dividends on deposits, lower fees, the Thank Use giveback program and many other member-exclusive benefits.
Credit Unions vs. Banks
Dupaco and its fellow Iowa credit unions return more than $100 million dollars annually to members through better rates and fewer fees compared to what they would have paid for similar services at a bank. And 40-percent of Iowa credit union loans are made to members with below average credit scores.
Banks, on the other hand, operate according to business models that empower them to cherry-pick profitable commercial loans and borrowers with pristine credit scores — all for the purpose of maximizing profits for their stockholders.
 The Seven Cooperative Principles
The Seven Cooperative Principles
As financial cooperatives, credit unions are guided by different principles than banks. So what exactly is a cooperative? Simply put, a cooperative is an organization that’s committed to improving its community and the lives of its members.
The cooperative model isn’t unique to credit unions. It exists and empowers multiple industries and business types. Here are the seven principles guiding every cooperative:
- Voluntary, Open Membership
Open to all without gender, social, racial, political, or religious discrimination. - Democratic Member Control
One member, one vote. - Member Economic Participation
Members contribute equitably to, and democratically control, the capital of the cooperative. The economic benefits of a cooperative operation are returned to the members, reinvested in the co-op, or used to provide member services. - Autonomy and Independence
Cooperatives are autonomous, self-help organizations controlled by their members. - Education, Training and Information
Cooperatives provide education and training for members so they can contribute effectively to the development of their cooperatives. They inform the general public about the nature and benefits of cooperation. - Cooperation Among Cooperatives
Cooperatives serve their members most effectively and strengthen the cooperative movement by working together through local, regional, national and international structures. - Concern for the Community
While focusing on member needs, cooperatives work for the sustainable development of their communities through policies accepted by their members.

